In the fields of Calif.'s Ventura County, some workers only speak Mixteco. The cultural and language barriers make it difficult for them to access health care. Reporter Julio Vaqueiro Borbolla tells the story of how he went about the difficult task of gaining their trust and telling their stories.
Health Equity & Social Justice
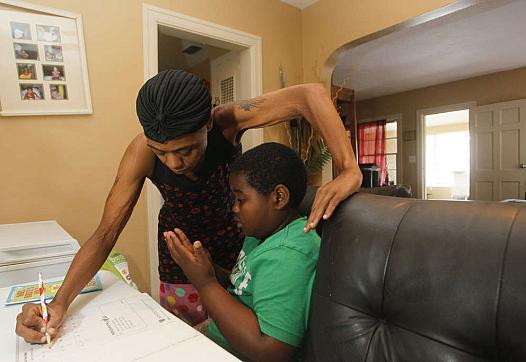
Using state and district personnel records, Times reporters compared teachers hired by the five resegregated schools with those hired at schools in wealthier, whiter neighborhoods. They found teachers in the whiter schools are more experienced and more likely to stay in their jobs.
Fresno County has some of the highest rates of STDs in the state. Public health officials say more needs to be done to reach all segments of the community.

Nearly 60 hospitals have closed in the U.S. since 2010. In reporting on how hospital closures affect poor patients in Rust Belt towns, reporter Sean Hamill found first-person accounts to be crucial. But backing up those stories with data and geographical comparisons also provided essential context.

In a town whose problems already include air pollution, water contamination and poverty, the California drought has spurred a growing health crisis, worsening respiratory conditions and burdening those with other illnesses, such as 49-year-old Manuel León.

Stigma is one reason that African Americans are less likely to get a colonoscopy. But a recent study found that doctors may be partly responsible as African Americans are more likely than any other racial and ethnic group to say that their doctor never recommended colon cancer screening.

During my fellowship project, I chose to focus on the impact of historical trauma and unresolved grief on the lives of Native peoples and ways that they are healing from the trauma and building resiliency. Here's what I learned along the way.

Elvia works as a medical interpreter in the Ventura County. Today, she is accompanying the occupational therapist Rachel Pile, who speaks only English. Every Monday, they work on 2-year-old Miguel’s therapy. His mother, Eulalia, only speaks and understands Mixteco.
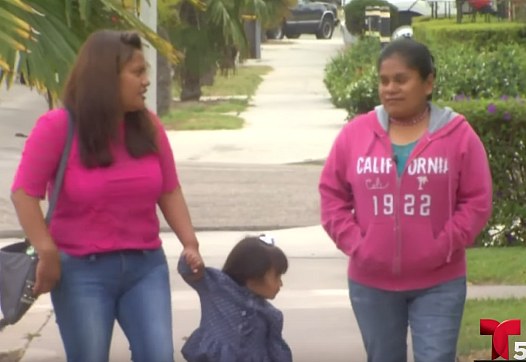
An estimated 165,000 indigenous Mexican immigrants live and work in the fields of California. Some 80% of them do not speak English or Spanish. This cultural and language barrier makes it difficult to treat mental illnesses in the community.

In the fields in the Ventura County some of the workers speak Mixteco. Many of these indigenous farm workers, like Florino, are living in the country illegally. They typically don’t have access to health care. Most of them face poor living conditions and backbreaking daily labor in the fields.